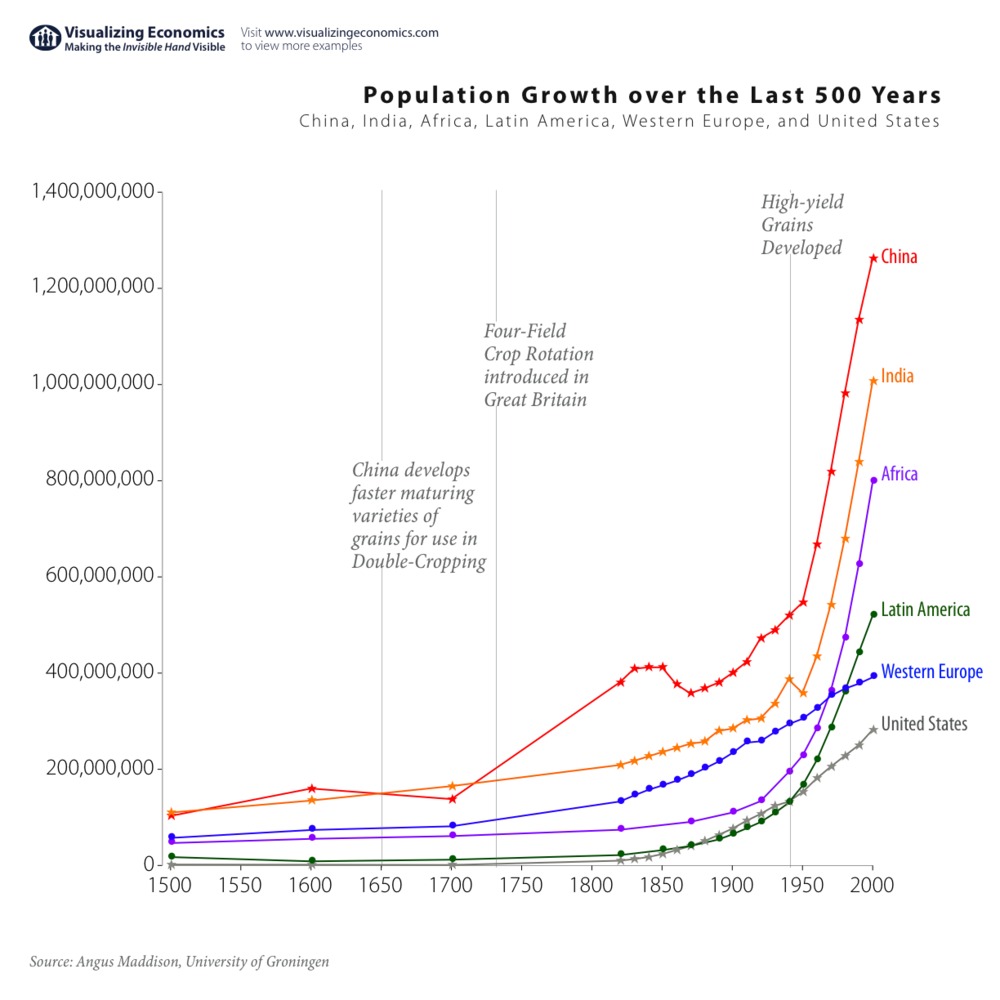
Global population growth is one of the most critical issues facing humanity today. The rapid expansion of the world's population has far-reaching implications for the environment, economies, and societies around the globe. Understanding the dynamics of this growth is essential to addressing the challenges it presents.
As the world's population continues to increase, it is vital to analyze the factors driving this growth and its potential consequences. By examining historical trends and current projections, we can gain insights into how global population growth will shape the future.
This article explores the complexities of global population growth, focusing on the key factors influencing it, the challenges it poses, and potential solutions. Whether you're a student, researcher, or simply someone interested in understanding this critical issue, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights.
Read also:50 Cent Net Worth 2024 The Rise Of A Hiphop Mogul
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Global Population Growth
- A Brief History of Global Population Growth
- Current Trends in Population Growth
- Factors Influencing Global Population Growth
- Environmental Impact of Population Growth
- Economic Effects of Population Growth
- Potential Solutions to Address Population Growth
- Challenges in Managing Population Growth
- Future Projections for Population Growth
- Conclusion
Introduction to Global Population Growth
Global population growth refers to the increase in the number of people living on Earth over time. This phenomenon has accelerated dramatically since the Industrial Revolution, with the global population reaching 8 billion in 2022. The rapid expansion of human populations has significant implications for resource availability, environmental sustainability, and social development.
The United Nations projects that the global population will reach 9.7 billion by 2050 and could stabilize at around 11 billion by the end of the century. However, these projections depend on various factors, including changes in fertility rates, mortality rates, and migration patterns.
Understanding the drivers and consequences of global population growth is crucial for policymakers, researchers, and individuals alike. By examining historical trends and current data, we can better prepare for the challenges ahead.
A Brief History of Global Population Growth
Throughout history, global population growth has been influenced by technological advancements, medical breakthroughs, and social changes. Before the 18th century, the global population grew slowly due to high mortality rates and limited agricultural productivity. However, the Industrial Revolution brought about significant improvements in healthcare, sanitation, and food production, leading to a population explosion.
From 1950 to 2000, the global population more than doubled, increasing from 2.5 billion to over 6 billion. This period of rapid growth was driven by declining mortality rates in developing countries and improved living conditions worldwide. However, fertility rates began to decline in many regions during the latter half of the 20th century, leading to slower population growth in some areas.
Today, population growth varies significantly across regions, with developing countries experiencing higher growth rates than developed nations. This disparity highlights the importance of regional analyses in understanding global population dynamics.
Read also:The Truth Behind Evelyns Role In Baldurs Gate 3
Current Trends in Population Growth
As of 2023, global population growth is slowing in many parts of the world. While the global population continues to increase, the rate of growth has declined significantly compared to previous decades. This trend is particularly evident in developed countries, where aging populations and low fertility rates are becoming more common.
However, population growth remains rapid in some developing regions, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia. These areas face significant challenges in providing adequate resources and infrastructure to support their growing populations. Understanding these regional differences is essential for developing effective policies to address population growth.
Factors Influencing Global Population Growth
Fertility Rates
Fertility rates are a key determinant of population growth. In general, higher fertility rates lead to faster population growth, while lower fertility rates result in slower growth or even population decline. Factors influencing fertility rates include cultural norms, economic conditions, and access to education and family planning services.
Many developed countries are experiencing below-replacement fertility rates, meaning that the average number of children per woman is less than 2.1. This trend has led to concerns about aging populations and shrinking workforces. In contrast, fertility rates remain relatively high in some developing regions, contributing to rapid population growth.
Mortality Rates
Mortality rates also play a significant role in population growth. Advances in healthcare and sanitation have led to declining mortality rates worldwide, particularly among children and infants. This has contributed to population growth, as more people survive to adulthood and reproduce.
However, improvements in mortality rates have slowed in some regions due to factors such as conflict, poverty, and inadequate healthcare systems. Addressing these challenges is essential for promoting sustainable population growth.
Migration Patterns
Migration patterns can also influence population growth, particularly in regions with significant levels of immigration or emigration. Countries experiencing net immigration tend to have higher population growth rates, while those with net emigration may see slower growth or even population decline.
Global migration patterns are shaped by economic opportunities, political stability, and environmental factors. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing policies that address both population growth and migration challenges.
Environmental Impact of Population Growth
Population growth has significant environmental consequences, including increased demand for natural resources, habitat destruction, and greenhouse gas emissions. As the global population continues to expand, these pressures are likely to intensify, threatening the sustainability of ecosystems worldwide.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of population growth is not uniform across regions. Developed countries, despite having lower population growth rates, often consume more resources and produce more emissions per capita than developing nations. Addressing these disparities is essential for promoting sustainable development.
Economic Effects of Population Growth
Population growth can have both positive and negative effects on economies. On the one hand, larger populations can provide a larger workforce and consumer base, driving economic growth. On the other hand, rapid population growth can strain resources, infrastructure, and public services, leading to economic challenges.
Developing countries, in particular, face significant challenges in providing education, healthcare, and employment opportunities for their growing populations. Addressing these challenges requires investments in infrastructure, education, and social services, as well as policies to promote sustainable economic development.
Potential Solutions to Address Population Growth
Addressing global population growth requires a multifaceted approach that includes improving access to education, promoting family planning services, and addressing economic disparities. By empowering individuals, particularly women, to make informed choices about family size, we can promote sustainable population growth.
Other potential solutions include investing in renewable energy, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, and addressing environmental degradation. These efforts can help mitigate the negative impacts of population growth and promote a more sustainable future.
Challenges in Managing Population Growth
Managing global population growth presents significant challenges, particularly in regions with limited resources and infrastructure. Political instability, poverty, and inadequate healthcare systems can hinder efforts to address population growth and its consequences.
Additionally, cultural and religious beliefs can influence fertility rates and attitudes toward family planning. Addressing these challenges requires sensitivity to local contexts and a commitment to promoting human rights and gender equality.
Future Projections for Population Growth
The United Nations projects that the global population will continue to grow, albeit at a slower rate, over the coming decades. By 2050, the global population is expected to reach 9.7 billion, with most of the growth occurring in developing regions. However, these projections are subject to uncertainty, as they depend on various factors, including changes in fertility rates, mortality rates, and migration patterns.
While population growth is expected to slow in many regions, some areas may experience continued rapid growth. Addressing these disparities will require coordinated efforts at the national and international levels.
Conclusion
Global population growth is a complex issue with far-reaching implications for the environment, economies, and societies worldwide. By understanding the factors driving this growth and its potential consequences, we can develop effective strategies to address the challenges it presents.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more information on related topics. Together, we can work toward a more sustainable and equitable future for all.